Solar energy financing has undergone a transformative revolution, introducing sophisticated commercial solar financing options that are reshaping business energy investments. Groundbreaking innovations in photovoltaic technology, coupled with innovative financial instruments, have reduced initial capital requirements by up to 60% while delivering enhanced energy yields. Forward-thinking organizations are leveraging power purchase agreements (PPAs), lease-to-own arrangements, and performance-based financing models to achieve immediate cost reductions without compromising their operational budgets.
The convergence of advanced energy storage solutions, smart grid integration, and flexible payment structures has created unprecedented opportunities for businesses to transition to sustainable energy systems. These developments have transformed solar installations from capital-intensive investments into strategic assets that generate both environmental and financial returns. Industry leaders implementing these solutions report average payback periods of 3-5 years, with some achieving break-even points in as little as 24 months through optimized financing structures.
Power Purchase Agreements: The Zero-Investment Solar Solution
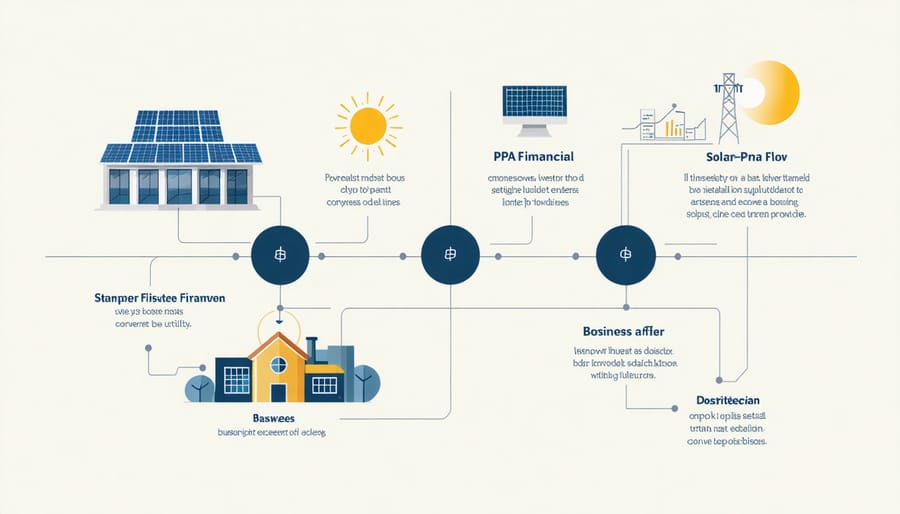
How PPAs Work for Your Business
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) offer a streamlined approach to transform your business energy costs without significant upfront investment. The process begins with a solar provider installing and maintaining a system on your property at no initial cost. Your business then agrees to purchase the generated electricity at a predetermined rate, typically lower than conventional utility prices, for a set period (usually 15-25 years).
Implementation follows a straightforward process: First, the provider assesses your facility’s solar potential and energy needs. Next, they design and install the system according to your specifications. Once operational, you only pay for the electricity produced, while the provider handles all maintenance and repairs.
The benefits are substantial: immediate reduction in electricity costs, protected rates against future utility price increases, and zero maintenance responsibilities. Additionally, PPAs allow businesses to demonstrate environmental leadership while maintaining predictable energy expenses.
For example, a manufacturing facility in Melbourne implemented a PPA and achieved 40% reduction in energy costs within the first year, while meeting 70% of their electricity needs through solar power. This arrangement enabled them to allocate capital to core business operations while still benefiting from renewable energy.
Risk Mitigation Through PPAs
Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) have emerged as a crucial risk mitigation tool in solar energy investments, offering businesses predictable energy costs and financial security. Through PPAs, organizations can lock in electricity rates for 15-25 years, effectively hedging against future utility rate increases and market volatility.
A well-structured PPA typically ensures that the solar developer bears responsibility for system performance, maintenance, and repairs, significantly reducing operational risks for the business. This arrangement allows companies to focus on their core operations while benefiting from clean energy and reduced utility costs.
For example, major retailers like Walmart and Target have successfully implemented PPAs across multiple facilities, achieving average energy cost savings of 20-30% while minimizing their exposure to electricity market fluctuations. These agreements often include performance guarantees, ensuring that if the system underperforms, the developer compensates the business for any shortfall in energy production.
PPAs also offer flexibility in contract terms, allowing organizations to customize agreements based on their specific needs and risk tolerance. Features like step-up pricing or buyout options can be incorporated to align with long-term financial strategies. This adaptability, combined with zero upfront costs, makes PPAs an attractive risk management solution for businesses transitioning to solar energy.
Solar Leasing: Flexible Solutions for Commercial Properties

Operating vs. Capital Leases
When considering solar installations, businesses must carefully evaluate their lease options. Operating leases treat solar installations as off-balance-sheet expenses, with regular payments classified as operating expenses. This structure allows companies to maintain cleaner balance sheets while benefiting from immediate tax deductions on lease payments.
Capital leases, alternatively, record the solar installation as an asset with corresponding liability on the balance sheet. While this increases reported assets and liabilities, it enables businesses to claim depreciation and interest expense deductions. Companies typically opt for capital leases when planning long-term solar investments and wanting to exercise greater control over the installation.
The choice between these lease structures often depends on financial goals and accounting preferences. Operating leases generally offer lower upfront costs and simplified accounting, making them attractive for businesses seeking flexibility. Capital leases, while more complex, provide advantages for companies planning to eventually own the system and maximize tax benefits.
For example, a retail chain might choose an operating lease to maintain financial ratios, while a manufacturing facility might prefer a capital lease for long-term energy independence.
Tax Benefits and Incentives
The federal Investment Tax Credit (ITC) remains one of the most significant financial incentives for commercial solar adoption, offering up to 30% of the total system cost in tax savings through 2032. Business owners can also benefit from accelerated depreciation through the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS), allowing them to maximize your solar ROI within the first five years of installation.
Many states offer additional incentives, including performance-based incentives (PBIs), Solar Renewable Energy Credits (SRECs), and property tax exemptions. Commercial property owners can often combine these with local utility rebates and grants, potentially reducing initial investment costs by 40-60%.
For manufacturing facilities implementing solar innovations, the Manufacturing Tax Credit provides additional benefits, while the Rural Energy for America Program (REAP) offers grants and loan guarantees specifically for agricultural businesses and rural small enterprises. These incentives, combined with reduced operational costs and increased property values, create a compelling financial case for commercial solar adoption.
Green Bonds and Solar Investment Funds
Leveraging Green Bonds
Green bonds have emerged as a powerful financing tool for businesses looking to implement solar energy projects. These fixed-income instruments specifically fund environmentally beneficial initiatives, offering companies a way to access capital markets while demonstrating their commitment to sustainability.
Organizations can issue green bonds to finance large-scale solar installations, with typical bond terms ranging from 5 to 15 years. The advantage lies in potentially lower interest rates compared to traditional financing, as investors often accept lower yields for environmentally responsible projects. For example, tech giant Apple’s $4.7 billion green bond initiative included significant solar power investments, resulting in 1.2 gigawatts of renewable energy capacity.
To leverage green bonds effectively, businesses should first establish clear project parameters and expected environmental benefits. Working with certified green bond verifiers ensures compliance with international standards, enhancing credibility with investors. The Climate Bonds Initiative reports that solar-focused green bonds have shown consistent growth, with a 20% year-over-year increase in issuance volume.
Companies can also participate in aggregate bond programs, where multiple smaller projects are bundled together, making this financing option accessible to mid-sized businesses pursuing solar initiatives.
Solar Investment Funds
Solar investment funds represent a strategic approach to financing solar projects by pooling capital from multiple investors. These funds typically operate as professionally managed investment vehicles that distribute both risks and returns across a diverse portfolio of solar installations. Investors can participate with varying levels of capital commitment, making solar investments accessible to a broader range of stakeholders.
The primary advantages of solar investment funds include reduced individual risk exposure, professional portfolio management, and economies of scale in project development. For example, a typical commercial solar fund might manage multiple installations across different geographical locations, effectively minimizing weather-related performance risks and maximizing overall returns.
Recent market data shows that solar investment funds have consistently delivered annual returns ranging from 6% to 12%, depending on the fund structure and project portfolio. These vehicles often combine tax benefits, power purchase agreement revenues, and renewable energy credits to optimize investor returns.
Institutional investors, including pension funds and insurance companies, have increasingly recognized solar investment funds as stable, long-term investment opportunities that align with ESG criteria while providing predictable cash flows. This growing institutional interest has helped expand the availability and sophistication of solar fund offerings in the market.
Property Assessed Clean Energy (PACE) Financing
Commercial PACE Benefits
Commercial Property Assessed Clean Energy (C-PACE) financing offers substantial advantages for property owners seeking to implement solar energy solutions. This innovative financing mechanism allows businesses to fund 100% of solar installation costs with no upfront capital investment, while spreading payments over extended terms of up to 30 years.
One of the primary benefits is that C-PACE assessments are tied to the property rather than the owner, transferring to new owners upon sale. This structure significantly reduces investment risk and enhances property value. The long-term fixed-rate financing typically results in positive cash flow from day one, as energy savings often exceed the assessment payments.
Property owners also benefit from immediate tax advantages, including the ability to deduct PACE payments as business expenses. The program’s non-accelerating structure protects property owners during ownership transitions, while the assessment’s senior lien status often leads to competitive interest rates.
For municipalities, C-PACE programs drive economic development, create local jobs, and support sustainability goals without requiring public funding. The program’s proven track record in multiple states demonstrates its effectiveness in facilitating large-scale solar adoption while maintaining financial stability for commercial properties.
Qualification and Implementation
To access PACE financing for solar innovations, property owners must first verify their eligibility by confirming their location falls within a PACE-enabled jurisdiction. The application process typically begins with a property assessment to determine the building’s energy improvement potential and estimated cost savings.
Key implementation steps include submitting a formal application through an authorized PACE administrator, providing detailed project specifications, and demonstrating the property’s financial standing. Property owners must work with qualified contractors who understand PACE requirements and can deliver compliant installations.
The approval process involves reviewing the property’s tax payment history, conducting a title search, and verifying that the proposed improvements meet program guidelines. Once approved, funding is secured through a PACE assessment, which is then repaid through property tax assessments over an extended period, typically 15-25 years.
Successful implementation requires coordination between multiple stakeholders: property owners, contractors, PACE administrators, and local government officials. Property owners should also ensure their mortgage lenders are notified and provide consent when required, as PACE assessments take priority in the property’s lien position.

Real-World Success Stories
Several groundbreaking solar financing implementations have demonstrated remarkable success across various commercial sectors. The IKEA Corporation’s ambitious solar initiative stands as a prime example, utilizing a power purchase agreement (PPA) to install solar arrays across 90% of their U.S. locations. This implementation resulted in a 35% reduction in energy costs within the first year, with projected savings of $89 million over ten years.
Another notable success story comes from Target Corporation, which leveraged innovative lease-back arrangements to deploy rooftop solar installations across 500 stores. By partnering with multiple investors through a structured financing approach, Target achieved an impressive ROI while maintaining operational control of their commercial solar innovations.
The Denver International Airport’s solar project showcases the power of public-private partnerships in solar financing. Through a combination of federal grants, tax incentives, and private investment, the airport installed 42,614 solar panels across 56 acres. This installation now generates 10 megawatts of power, covering approximately 6% of the airport’s total electricity consumption and resulting in annual savings of $1.2 million.
Walmart’s solar implementation strategy demonstrates the effectiveness of multi-phase financing approaches. By utilizing a combination of direct ownership and third-party financing models, they’ve successfully installed solar panels on over 500 facilities. Their phased approach allowed for careful evaluation of performance metrics and continuous optimization of financing structures, resulting in a 35% internal rate of return across their solar portfolio.
These success stories highlight how tailored financing solutions, combined with strategic implementation planning, can deliver substantial returns while advancing sustainability goals.
The evolution of solar financing continues to reshape the renewable energy landscape, offering increasingly flexible and accessible options for businesses of all sizes. As technology costs decrease and financing models mature, solar investments are becoming more attractive and feasible for organizations seeking sustainable energy solutions. The emergence of innovative financing structures, including green bonds, solar PPAs, and hybrid models, provides unprecedented opportunities for businesses to transition to clean energy while maintaining strong financial performance.
Looking ahead, the solar financing sector is poised for continued growth and innovation. The combination of favorable policies, technological advancements, and growing environmental consciousness suggests a bright future for solar investments. Organizations that act now to explore and implement solar financing solutions will be well-positioned to benefit from reduced energy costs, enhanced sustainability credentials, and improved competitive advantage in an increasingly carbon-conscious market.

