The global transition to renewable energy transportation marks a pivotal shift in how businesses and cities approach mobility solutions. As electric vehicles, hydrogen fuel cells, and sustainable mass transit systems reshape our transportation infrastructure, organizations face both unprecedented opportunities and complex implementation challenges. Industry leaders are witnessing a convergence of policy initiatives, technological breakthroughs, and market demands that are accelerating the adoption of clean transportation solutions across supply chains and urban centers.
Recent data reveals that renewable energy transportation investments reached $501 billion globally in 2023, signaling a transformative moment for commercial fleet operators, urban planners, and transportation authorities. This surge in sustainable mobility solutions isn’t merely an environmental imperative—it represents a strategic advantage for businesses positioning themselves at the forefront of the clean energy revolution.
For decision-makers navigating this rapidly evolving landscape, understanding the intersection of renewable energy policies, infrastructure requirements, and emerging technologies has become crucial for long-term success. This comprehensive analysis explores how organizations can capitalize on renewable transportation initiatives while addressing implementation challenges and maximizing return on investment in sustainable mobility solutions.
Current Renewable Energy Policies Driving Transportation Change
EV Incentives and Infrastructure Mandates
Government incentives and infrastructure mandates play a crucial role in accelerating EV adoption across the transportation sector. Federal tax credits of up to $7,500 for new electric vehicles and $4,000 for used EVs have significantly influenced purchase decisions for both fleet operators and individual consumers. These incentives, combined with state-level rebates and grants, can reduce the total cost of ownership by 20-30% over the vehicle’s lifetime.
Infrastructure requirements are evolving rapidly, with many jurisdictions now mandating EV charging capabilities in new commercial construction. The National Electric Vehicle Infrastructure (NEVI) Formula Program has allocated $5 billion to states for creating a nationwide charging network, focusing on major transportation corridors and urban centers. Commercial property owners can access matching funds covering up to 80% of installation costs for public charging stations.
For businesses, understanding these incentives is essential for strategic planning. Many organizations are leveraging available funding to install workplace charging stations, which not only serves employees but can generate additional revenue through public access. Local utilities often provide special rate structures and technical assistance for commercial charging installations, further enhancing the business case for EV infrastructure investment.
Grid Integration Policies
Modern grid integration policies are reshaping how renewable energy interfaces with transportation infrastructure. Governments worldwide are implementing regulatory frameworks that facilitate the seamless integration of renewable power sources with electric vehicle charging networks and public transit systems. These policies typically mandate specific interconnection standards, grid modernization requirements, and energy storage provisions to ensure reliable power delivery for transportation applications.
Key policy measures include feed-in tariffs for renewable energy producers, infrastructure development incentives, and standardization requirements for charging stations. Many jurisdictions have adopted smart grid requirements that enable real-time load management and dynamic pricing, particularly beneficial for commercial fleet operators and transit authorities.
For businesses, these policies create opportunities through tax incentives, grants, and public-private partnership frameworks. Organizations can leverage these initiatives to develop charging infrastructure, implement vehicle-to-grid systems, and participate in demand response programs. Progressive municipalities are also introducing zoning regulations that require new commercial developments to include renewable energy infrastructure for transportation purposes, setting the stage for future expansion of sustainable mobility solutions.
Commercial Impact and Business Opportunities
Fleet Electrification Benefits
Transitioning to electric fleets offers organizations substantial operational and financial advantages while advancing sustainability goals. Companies implementing fleet electrification typically experience a 20-30% reduction in total cost of ownership over vehicle lifespans, primarily through lower fuel and maintenance costs. Electric vehicles require fewer moving parts and fluid changes, resulting in reduced downtime and maintenance expenses.
Beyond cost savings, electric fleets provide significant environmental benefits, helping organizations meet corporate sustainability targets and comply with emerging regulations. Studies show that electric fleet vehicles can reduce greenhouse gas emissions by up to 50% compared to conventional vehicles, even when accounting for electricity generation.
Fleet electrification also enhances operational efficiency through advanced telematics and predictive maintenance capabilities. Modern electric vehicles provide real-time data on vehicle performance, route optimization, and charging status, enabling better fleet management and resource allocation.
Organizations benefit from improved brand reputation and customer loyalty, as consumers increasingly favor environmentally responsible businesses. Additionally, electric fleets help future-proof operations against volatile fuel prices and stringent environmental regulations.
Early adopters have reported enhanced driver satisfaction due to reduced noise, smoother operation, and improved cabin air quality. These benefits contribute to better employee retention and reduced training costs. Government incentives, including tax credits and grants, further improve the business case for fleet electrification, often reducing initial investment costs by 20-40%.

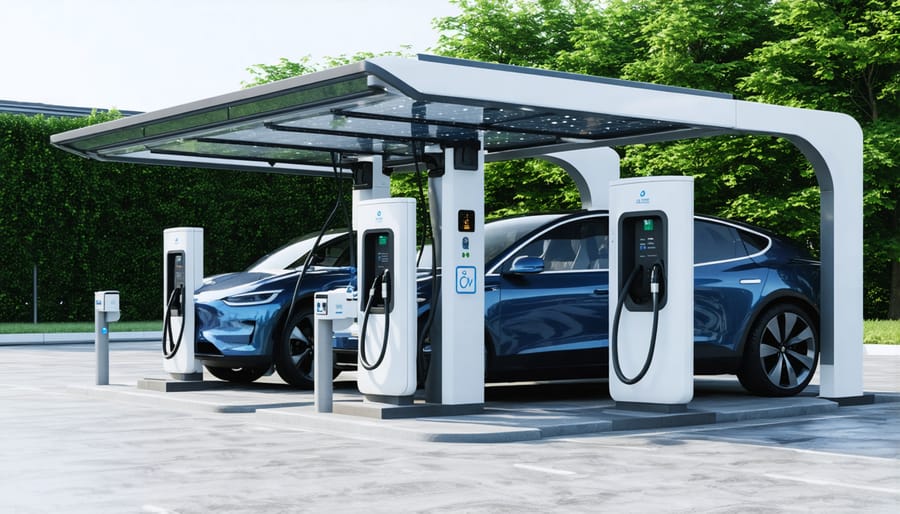
Solar-Powered Charging Solutions
Solar-powered charging infrastructure represents a significant advancement in sustainable transportation, combining renewable energy generation with electric vehicle charging capabilities. These integrated systems typically consist of solar canopies or arrays connected to EV charging stations, providing clean energy directly to vehicles while offering additional benefits such as weather protection and energy independence.
Leading organizations have successfully implemented solar charging solutions with compelling results. The Contra Costa County administration building in California installed a solar charging system that generates 1.7 megawatts of power, supporting their EV fleet while reducing operational costs by approximately 20% annually. Similarly, IKEA’s solar-powered charging stations across multiple locations demonstrate the commercial viability of these systems.
The implementation process involves strategic planning, including site assessment, solar capacity calculation, and integration with existing electrical infrastructure. Modern solar charging stations incorporate smart energy management systems that optimize power distribution between direct solar usage, grid supply, and optional battery storage. This flexibility ensures reliable charging availability regardless of weather conditions.
From a business perspective, solar-powered charging solutions offer multiple revenue streams. Beyond charging fees, excess energy can be sold back to the grid, while solar renewable energy credits (SRECs) provide additional income opportunities. Government incentives, including tax credits and grants, can significantly reduce initial installation costs, improving the return on investment timeline.
As technology advances, newer solutions include bifacial solar panels and intelligent load management systems, enhancing overall system efficiency and reliability while maximizing space utilization.

Implementation Challenges and Solutions
Infrastructure Development
The expansion of renewable energy transportation infrastructure presents both challenges and opportunities for stakeholders across the energy and transportation sectors. The development of urban charging infrastructure requires substantial investment and careful planning to meet growing demand while ensuring grid stability.
Power grid capacity remains a critical consideration as the adoption of electric vehicles accelerates. Utilities are implementing smart grid technologies and demand response systems to manage peak loads effectively. These innovations help distribute power more efficiently and prevent network overload during high-demand periods.
Strategic placement of charging stations is essential for maximizing utilization and return on investment. Commercial centers, workplace parking facilities, and residential complexes are prime locations for charging infrastructure deployment. Many businesses are partnering with charging network operators to offer convenient charging solutions while creating new revenue streams.
Grid reinforcement projects are underway in many regions to support the increased electrical demand. These upgrades include the installation of high-capacity transformers, advanced monitoring systems, and energy storage solutions. Such improvements enhance grid resilience and enable the integration of renewable energy sources.
The development of ultra-fast charging technology is addressing range anxiety concerns while creating new opportunities for businesses along major transportation corridors. These installations require significant power capacity but provide crucial support for long-distance travel and commercial fleet operations.
Cost Management Strategies
Effective cost management in renewable energy transportation requires a strategic combination of funding mechanisms and operational efficiency measures. Organizations can leverage various financial instruments, including government grants, tax incentives, and public-private partnerships to offset initial implementation costs. The U.S. Department of Energy’s Clean Cities program, for example, provides matching funds for fleet conversion projects, reducing the financial burden on businesses.
Smart financing options such as power purchase agreements (PPAs) and energy-as-a-service models enable organizations to implement renewable transportation solutions with minimal upfront investment. These arrangements typically include maintenance and performance guarantees, ensuring predictable operational costs over the long term.
Cost reduction strategies should focus on both immediate and long-term savings. Organizations can optimize their renewable transportation systems through:
– Fleet rightsizing and route optimization
– Regular maintenance scheduling to prevent costly repairs
– Energy storage integration to maximize renewable energy usage
– Bulk purchasing agreements for renewable fuels or charging infrastructure
– Employee training programs to ensure efficient system operation
Data-driven decision making plays a crucial role in cost management. Modern fleet management systems can track energy consumption patterns, identify inefficiencies, and suggest optimization opportunities. Organizations that implement these systems typically report 15-25% reduction in operational costs within the first year.
The key to successful cost management lies in developing a comprehensive strategy that balances initial investment with long-term operational savings, while taking advantage of available financial incentives and technological innovations.
Future Policy Directions
The landscape of renewable energy transportation policy is rapidly evolving, with several key trends shaping the future of sustainable mobility. Governments worldwide are increasingly adopting comprehensive frameworks that integrate transportation electrification with broader renewable energy accessibility initiatives.
Carbon pricing mechanisms are expected to become more prevalent, with many jurisdictions implementing or expanding existing programs to incentivize clean transportation alternatives. These policies will likely include graduated fee structures that reward early adopters while maintaining pressure on traditional fossil fuel-dependent vehicles.
Infrastructure development policies are shifting toward mandatory charging station requirements for new commercial developments and parking facilities. Many regions are introducing legislation requiring a minimum percentage of parking spaces to include EV charging capabilities, with some proposals reaching up to 20% by 2030.
Financial incentives are evolving beyond simple purchase subsidies to include performance-based rewards for fleet operators who achieve specific emission reduction targets. This approach encourages ongoing commitment to renewable transportation solutions rather than one-time adoption decisions.
Corporate fleet electrification mandates are gaining traction, with several major economies proposing requirements for businesses to transition their vehicle fleets to zero-emission alternatives within the next decade. These policies often include provisions for charging infrastructure and grid integration support.
Smart grid integration policies are becoming increasingly sophisticated, with regulations promoting vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology and dynamic pricing models. These frameworks will enable better load management and create new revenue opportunities for fleet operators through energy storage and grid services.
Looking ahead, policy frameworks are expected to emphasize cross-sector collaboration, linking transportation electrification with renewable energy generation and storage solutions. This integrated approach will help create more resilient and efficient energy systems while accelerating the transition to sustainable transportation.
The transition to renewable energy in transportation represents a pivotal shift in how we approach mobility and sustainability in the modern era. Throughout this exploration, we’ve seen how electric vehicles, sustainable mass transit systems, and innovative charging infrastructure are reshaping our transportation landscape. The integration of renewable energy sources into transportation not only reduces carbon emissions but also creates substantial economic opportunities for businesses and municipalities.
Key takeaways emphasize the importance of strategic planning and phased implementation. Organizations can begin by conducting comprehensive energy audits, identifying high-impact areas for renewable integration, and developing clear transition timelines. The success stories we’ve examined demonstrate that combining multiple renewable solutions – from solar-powered charging stations to hydrogen fuel cells – often yields the best results.
To move forward effectively, stakeholders should focus on three critical actions: investing in scalable infrastructure, fostering public-private partnerships, and leveraging available government incentives. Business leaders and facility managers should particularly consider pilot programs to test renewable transportation solutions before full-scale deployment.
As technology continues to advance and costs decrease, the business case for renewable energy transportation becomes increasingly compelling. Organizations that act now to implement sustainable transportation solutions will likely find themselves at a significant competitive advantage, benefiting from both operational cost savings and enhanced corporate reputation. The future of transportation is undoubtedly renewable, and the time to begin this transformation is now.

