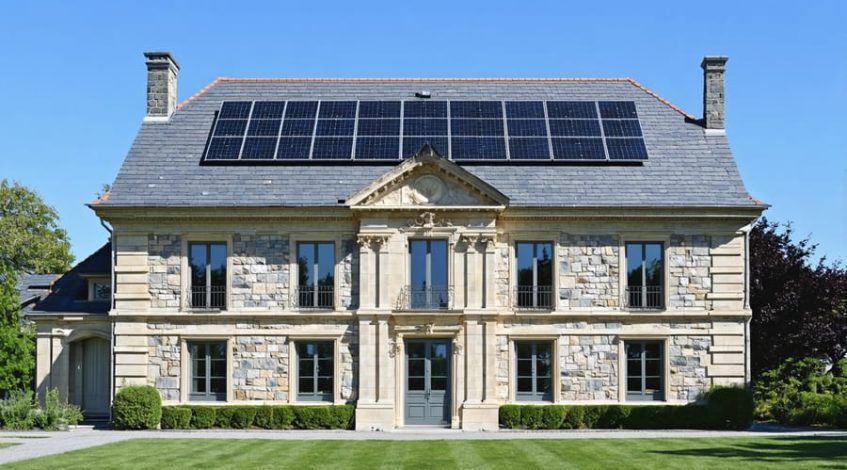
Balancing renewable energy adoption with preserving historic architecture demands innovative solutions that respect both sustainability and cultural heritage. Historic districts across the globe now successfully integrate solar technology through low-profile panels, specialized mounting systems, and carefully planned installations that maintain architectural integrity. Property owners achieve up to 30% energy cost reduction while adhering to preservation guidelines by implementing reversible mounting solutions, utilizing secondary rooflines, and positioning panels on non-street-facing elevations.
Recent advancements in solar technology, including thin-film panels and solar slate tiles, offer historically appropriate alternatives that satisfy preservation boards while delivering substantial energy benefits. These solutions demonstrate that historic properties can embrace clean energy without compromising their authentic character or historical significance. Leading preservation organizations now actively support solar integration, recognizing that sustainable energy practices ensure these landmarks remain viable and valuable for future generations.
Successful implementation requires early engagement with preservation committees, detailed documentation of installation plans, and partnership with solar providers experienced in historic property modifications. This proactive approach streamlines approval processes and ensures optimal system performance while maintaining historic district guidelines.
Navigating Historic District Regulations
Key Compliance Requirements
Solar panel installations in historic districts must adhere to strict preservation guidelines while accommodating modern energy needs. The primary requirement is maintaining the building’s historic character, which typically means panels should not be visible from primary public views. Installations must be reversible, causing no permanent damage to historic materials or architectural features.
Height restrictions often limit panel placement to positions below the ridgeline of sloped roofs. Setback requirements generally mandate panels be installed at least 10 feet from the roof’s edge on primary facades. Color matching between panels, mounting systems, and existing roof materials is frequently required to minimize visual impact.
Documentation requirements include detailed site plans, elevation drawings, and photo simulations showing the proposed installation from multiple viewpoints. Many jurisdictions require certification that the installation will not compromise the structural integrity of historic buildings. Additionally, property owners must demonstrate that alternative locations, such as secondary roofs or ground-mounted systems, have been evaluated before proposing installations on primary historic facades.
Mounting systems must be minimally invasive, and any penetrations through historic materials must be properly sealed and weatherproofed to prevent deterioration. Regular maintenance plans are typically required as part of the approval process.
Working with Preservation Boards
Successful collaboration with preservation boards requires a strategic approach and thorough preparation. Begin by researching the specific guidelines and precedents established by your local historic preservation committee. Schedule a preliminary consultation before submitting formal plans to understand their concerns and requirements.
Document how your proposed solar installation aligns with preservation standards, emphasizing minimal visual impact and reversibility. Present detailed renderings showing multiple viewpoints of the installation, particularly from street level. Include examples of successful solar implementations in similar historic properties.
Consider compromises that balance energy efficiency with preservation goals. This might include using solar panels that match roof colors, installing panels on less visible roof sections, or utilizing ground-mounted systems where appropriate. Prepare a comprehensive preservation plan that addresses how the installation will protect historic materials and architectural features.
Build support for your project by engaging preservation experts early in the planning process. Their expertise can help develop solutions that satisfy both renewable energy goals and historic preservation requirements. Remember that preservation boards often appreciate applicants who demonstrate respect for historic integrity while pursuing sustainable innovations.
Innovative Solar Solutions for Historic Buildings
Low-Profile Solar Systems
Recent advancements in innovative solar solutions for heritage buildings have introduced several low-profile options that minimize visual impact while maximizing energy generation. Solar slate tiles and thin-film panels can be integrated directly into existing roofing materials, maintaining the architectural integrity of historic structures. These systems lie flush with the roof surface, eliminating the raised appearance of traditional solar arrays.
Modern solar shingles, designed to match period-appropriate materials, offer another discrete solution. These units replicate the look of traditional slate, clay, or wooden shingles while incorporating photovoltaic technology. Additionally, some manufacturers now produce transparent solar panels that can be incorporated into skylights or glass features, preserving original design elements while generating clean energy.
For flat-roofed historic buildings, ballasted systems set back from the roof edge provide an effective solution. These installations remain hidden from street level, satisfying preservation requirements while delivering substantial energy benefits. When combined with smart mounting systems and careful placement strategies, these low-profile options enable historic properties to embrace sustainable technology without compromising their cultural significance.
Solar Slate and Tile Integration
Recent advancements in the evolution of solar technology have produced innovative solutions that seamlessly integrate with historic architecture. Solar slate and tile products now replicate traditional roofing materials while incorporating photovoltaic technology, offering a practical compromise between preservation and sustainability.
These specialized solar products are designed to match the appearance, size, and texture of historic slate, clay, or concrete tiles. Manufacturers achieve this through advanced manufacturing processes that create solar cells with customized colors, patterns, and surface finishes. The result is a solar installation that maintains the architectural integrity of historic buildings while generating clean energy.
Leading products in this category include solar slate tiles that feature monocrystalline cells embedded within durable composite materials, and solar roof tiles that incorporate thin-film technology. These elements can be installed alongside existing roofing materials, allowing for partial solar coverage that preserves the building’s historic character.
Installation costs typically range from 15-30% higher than conventional solar panels, but the aesthetic benefits and preservation compliance often justify the investment for historic properties. Many jurisdictions now specifically approve these integrated solutions for historic district applications.

Alternative Placement Strategies
Several innovative placement strategies allow property owners to incorporate solar panels while preserving historic architectural features. Ground-mounted arrays positioned in less visible rear yards offer an effective alternative to roof installations. These systems can be partially concealed by strategic landscaping or period-appropriate fencing while maintaining optimal sun exposure.
Carport and auxiliary structure installations present another viable solution. By mounting panels on newly constructed period-compatible structures, owners can generate clean energy without modifying historic buildings. Some properties have successfully integrated solar arrays into existing garden pergolas or created dedicated solar pavilions that complement historic aesthetics.
Vertical wall mounting on non-street-facing facades provides another discrete option, particularly for buildings with suitable southern exposure. These installations can be designed to mirror existing architectural elements or screened by traditional features like lattice work.
For properties with sufficient land, solar gardens located away from historic structures offer maximum generation potential while completely preserving building integrity. Some districts have implemented community solar projects, allowing multiple historic properties to benefit from a single, appropriately-sited installation.
When roof mounting is necessary, low-profile systems installed on less visible rear slopes or behind existing parapets can minimize visual impact while maintaining energy production efficiency.
Success Stories and Case Studies
Commercial Heritage Buildings
Commercial properties across the United States have successfully demonstrated that solar installations and historic preservation can coexist harmoniously. The Bullitt Center in Seattle, a century-old restored building, now operates as a net-zero energy facility through innovative solar panel placement that respects its historic façade. The installation generates 60% of the building’s energy needs while maintaining its architectural integrity.
In Boston, the historic Leather District showcases how rooftop solar arrays can be integrated without compromising the area’s distinctive character. The district’s Victorian-era industrial buildings now feature carefully positioned solar panels, invisible from street level, generating substantial energy savings for tenants while preserving the neighborhood’s historic appeal.
Another notable example is Charleston’s Historic Market District, where merchants collaborated with preservation boards to implement solar solutions that power multiple businesses. The installation utilizes low-profile panels and specialized mounting systems that minimize visual impact while maximizing energy production.
The success of these commercial properties has created a blueprint for others to follow. Key factors include early engagement with preservation boards, selection of appropriate solar technologies, and careful consideration of panel placement. These projects demonstrate that commercial buildings can achieve significant energy savings while honoring their historical significance, often resulting in increased property values and reduced operating costs.

Historic Residential Properties
Several successful residential solar installations in historic districts demonstrate how modern technology can coexist with architectural preservation. In Boston’s Beacon Hill district, homeowners worked with preservation boards to install low-profile panels on a rear-facing roof slope, maintaining the property’s historic character while achieving 75% energy offset. The installation utilized black-on-black panels with specialized mounting hardware to minimize visual impact from street level.
A Victorian-era home in Charleston’s Historic District showcases innovative panel placement behind existing parapets, completely concealing the system from public view while generating sufficient power for the 2,800-square-foot residence. The project received approval after presenting detailed visibility studies and implementing special screening methods.
In Savannah, Georgia, a row of townhouses dating to the 1850s successfully integrated solar arrays using a combination of roof-mounted and carport installations. The project team employed period-appropriate screening materials and strategic placement to preserve the historic streetscape while providing modern energy benefits to residents.
A notable installation in Alexandria, Virginia’s Old Town district utilized solar shingles rather than traditional panels, maintaining the original roof’s appearance while incorporating renewable energy technology. This approach has become a model for other historic districts seeking to balance preservation requirements with sustainability goals.
These case studies demonstrate that with careful planning and appropriate design considerations, historic homes can successfully adopt solar technology while preserving their architectural integrity.
Investment and ROI Considerations
Special Incentives and Grants
Property owners interested in installing solar panels in historic districts can access various financial incentives and grants specifically designed for preservation-conscious renewable energy projects. The Federal Historic Preservation Tax Credit program offers a 20% tax credit for qualifying rehabilitation expenses, which can include solar installations that meet preservation guidelines.
Many state historic preservation offices provide matching grants ranging from $5,000 to $50,000 for sustainable upgrades to historic properties. These funds often require adherence to specific installation standards and may cover up to 50% of project costs. Additionally, the National Trust for Historic Preservation’s Sustainable Communities Fund offers grants specifically for green energy initiatives in historic districts.
Local governments frequently provide property tax abatements and expedited permitting processes for solar installations on historic buildings. Some municipalities offer specialized incentives that combine historic preservation funds with renewable energy credits, creating comprehensive financial packages for property owners.
The Department of Energy’s Historic Buildings Energy Efficiency Guide program provides technical assistance grants that can cover preliminary assessments and design plans. These funds help ensure solar installations meet both energy efficiency goals and preservation requirements.
Organizations should also investigate utility company incentives, which may offer additional rebates for historic properties implementing solar solutions. Combined with federal and state solar investment tax credits, these incentives can significantly reduce the initial investment costs while preserving historical integrity.
Long-term Value Analysis
The integration of solar panels in historic districts presents a compelling long-term value proposition when analyzed through both energy savings and property value metrics. Studies show that buildings equipped with solar installations can maintain historic character while reducing costs through average energy savings of 40-60% annually.
Property valuations in historic districts typically command a premium of 5-10% over comparable properties in non-historic areas. Solar installations can enhance this premium further, with data indicating an additional 4.1% increase in property value. This dual benefit creates a unique investment opportunity where both historical significance and sustainable technology contribute to asset appreciation.
The ROI timeline for solar installations in historic properties averages 5-7 years, considering current energy prices and available tax incentives. Many property owners report breaking even faster through combination of reduced utility costs, increased property value, and various preservation grants specific to historic buildings implementing sustainable solutions.
Financial institutions increasingly recognize this value proposition, offering preferential lending terms for historic properties incorporating solar technology. This trend reflects growing market confidence in the long-term economic viability of solar installations in heritage contexts, further strengthening the investment case for property owners and developers.
The integration of solar panels in historic districts represents a delicate balance between preserving our architectural heritage and embracing sustainable energy solutions. As demonstrated throughout this discussion, successful implementation requires careful planning, stakeholder collaboration, and innovative approaches to design and installation. By following established guidelines, working closely with preservation boards, and utilizing modern solar technologies designed for historic properties, building owners can achieve both their sustainability goals and maintain the integrity of historic structures.
The financial benefits of solar installation, including tax incentives, reduced energy costs, and potential property value increases, make a compelling case for investment. Moreover, the growing number of successful case studies across various historic districts proves that solar integration can be achieved without compromising architectural character.
Moving forward, property owners and stakeholders should take proactive steps by consulting with preservation experts and solar professionals early in the planning process. Developing a comprehensive strategy that addresses both preservation requirements and energy needs will ensure successful project outcomes. As solar technology continues to advance, we can expect even more aesthetically compatible solutions for historic properties.
By embracing these sustainable innovations while respecting historical significance, we create a blueprint for future generations to follow, demonstrating that preservation and progress can coexist harmoniously. The time to act is now, as we work together to protect our architectural heritage while building a more sustainable future.

