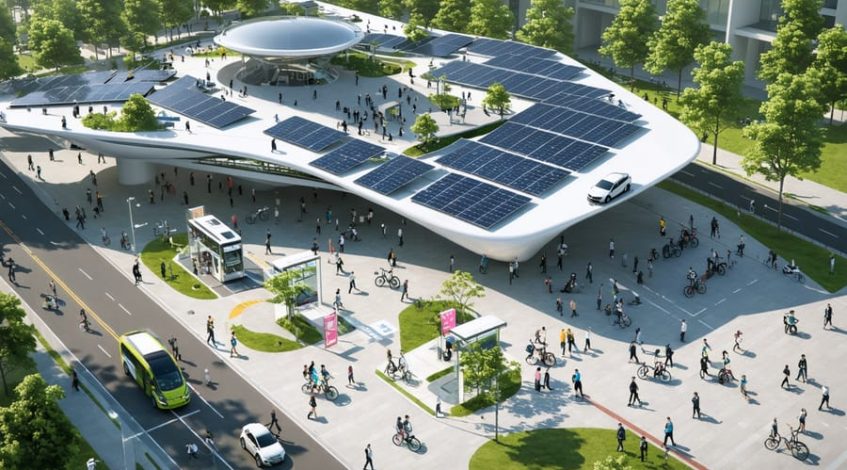
Urban solar power stands at the forefront of modern energy transformation, revolutionizing how cities harness and distribute clean energy across dense metropolitan landscapes. As commercial buildings and public infrastructure evolve into power generation hubs, innovative sustainable transit solutions are reshaping urban energy dynamics. The integration of photovoltaic systems into existing city infrastructure not only addresses growing energy demands but also creates resilient power networks capable of supporting smart city initiatives.
Recent advancements in solar technology, coupled with declining installation costs, have made urban solar installations increasingly viable for businesses and municipalities. These systems now deliver compelling returns on investment while contributing to municipal sustainability goals and carbon reduction targets. From rooftop arrays on commercial buildings to solar canopies over parking structures, urban solar applications are transforming underutilized spaces into valuable energy assets.
The strategic implementation of solar power in urban environments represents a critical step toward energy independence and environmental stewardship, while simultaneously providing economic benefits through reduced operational costs and enhanced grid stability. For facility managers and urban planners, this presents an unprecedented opportunity to modernize infrastructure while creating more sustainable, resilient cities.
The Architecture of Solar Mobility Hubs
Solar Integration Design
Modern mobility hub structures require sophisticated solar integration systems that maximize energy generation while maintaining architectural integrity. The standard configuration typically includes high-efficiency photovoltaic panels rated at 400-450W per module, with an average system size ranging from 50kW to 200kW depending on the facility’s dimensions.
These installations commonly utilize bifacial solar panels, which capture both direct sunlight and reflected light from surrounding surfaces, increasing energy yield by 5-15% compared to traditional modules. The mounting systems are designed to withstand urban environmental challenges, featuring corrosion-resistant materials and wind-load ratings suitable for rooftop installations.
Integration specifications typically include:
– Minimum roof load capacity of 25kg/m²
– Smart inverter systems with 98%+ efficiency
– Optimizers for partial shading conditions
– Remote monitoring capabilities
– Grid connection equipment rated for commercial power requirements
The design must account for existing HVAC systems, maintaining service access while maximizing solar coverage. Modern installations incorporate cable management systems that protect wiring from environmental exposure while maintaining aesthetic appeal. Temperature sensors and monitoring equipment are strategically placed to ensure optimal system performance and facilitate predictive maintenance protocols.
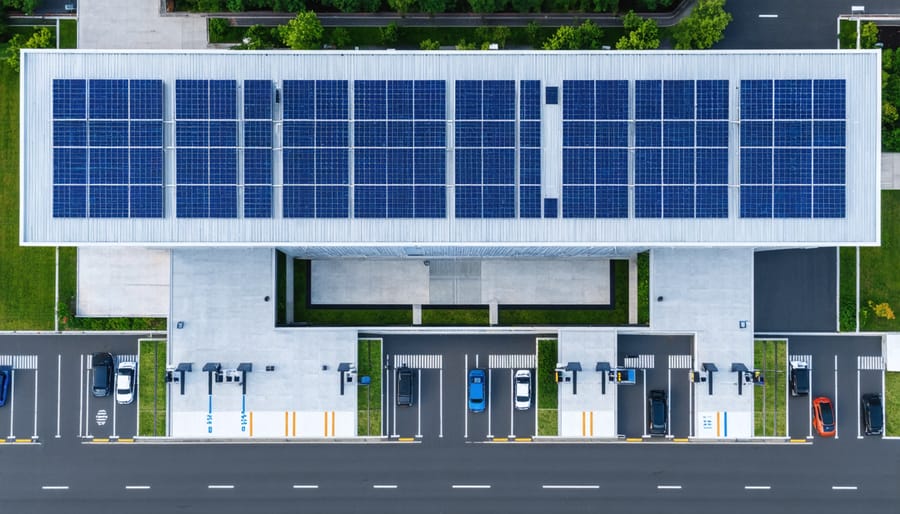

Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage solutions play a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency and reliability of urban solar power systems. Modern battery technologies, particularly lithium-ion systems, have become increasingly sophisticated, offering greater storage capacity and longer lifespans than ever before. These systems enable businesses and facilities to store excess solar energy generated during peak production hours for use during nighttime or cloudy periods.
Commercial-scale battery storage systems typically range from 50kWh to several MWh, depending on facility requirements. Advanced power management systems integrate seamlessly with these storage solutions, utilizing smart algorithms to optimize energy distribution and consumption patterns. This intelligence allows for automated load shifting, demand response participation, and strategic energy arbitrage opportunities.
The implementation of storage solutions has shown significant ROI potential, with many facilities reporting 20-30% reductions in peak demand charges. For example, the Metropolitan Business Center in San Francisco achieved a 25% reduction in energy costs after installing a 500kWh battery system alongside their solar array.
Modern storage solutions also feature advanced safety protocols and monitoring capabilities. Battery management systems (BMS) continuously monitor temperature, voltage, and current levels, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. Many systems now offer remote monitoring and control capabilities, allowing facility managers to optimize their energy usage in real-time through mobile applications or desktop interfaces.
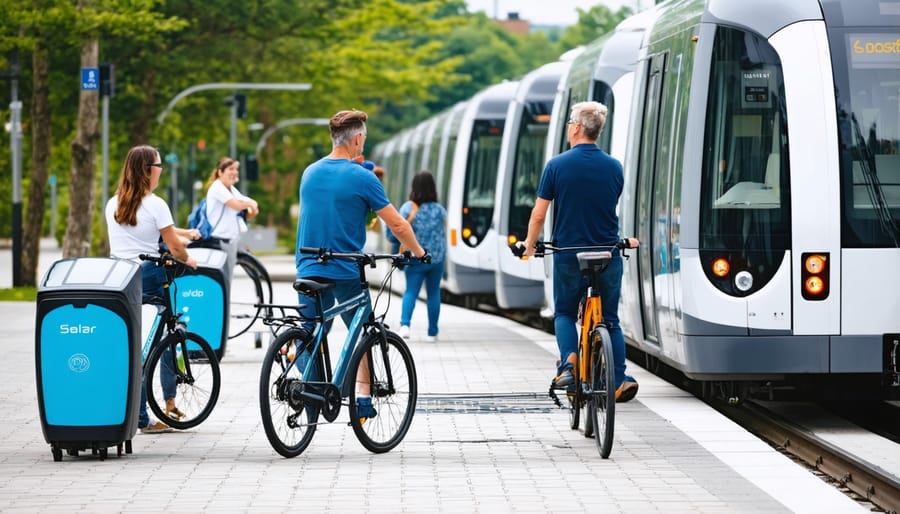

Multi-Modal Transportation Benefits
Electric Vehicle Charging Infrastructure
Solar power integration in urban environments has become increasingly vital for supporting the growing electric vehicle (EV) charging infrastructure. Modern solar-powered charging stations can deliver Level 2 charging capabilities of up to 19.2 kW per port, with advanced systems incorporating battery storage to ensure consistent power delivery even during non-peak solar hours.
A typical urban solar installation powering EV chargers requires approximately 15-20 square meters of panel surface area per charging port to generate sufficient electricity for daily operations. These systems can be configured to support multiple charging stations simultaneously, with smart load management systems optimizing power distribution based on real-time demand and solar generation.
Commercial installations commonly feature canopy-mounted solar arrays that serve dual purposes: generating power for EV charging while providing covered parking. These setups typically achieve 20-30% higher efficiency compared to traditional grid-only charging stations, resulting in significant operational cost savings.
For facility managers, integrating solar-powered EV charging infrastructure can qualify for various federal and state incentives, potentially reducing initial investment costs by 30-40%. The system’s payback period typically ranges from 5-7 years, depending on local utility rates and charging demand patterns.
E-Bike and Micromobility Support
Urban solar installations increasingly support the growing demand for e-bike and micromobility charging infrastructure. Dedicated solar-powered charging stations provide convenient power access for e-bikes, e-scooters, and other small electric vehicles, encouraging sustainable urban transportation options while reducing grid dependency.
These facilities typically include covered parking structures equipped with solar panels, secure bike racks with integrated charging ports, and smart monitoring systems that track usage patterns and energy consumption. A standard installation can support 15-20 vehicles simultaneously, with quick-charging capabilities that enable a full charge within 2-3 hours.
Many cities are incorporating these solar-powered micromobility hubs into existing transportation networks. For example, Portland’s Green Loop initiative features solar-powered e-bike stations that serve over 500 users daily while generating excess power for nearby facilities. Similarly, Barcelona’s solar mobility points combine EV charging with micromobility support, demonstrating how integrated solutions can maximize space utilization in dense urban areas.
The investment in solar-powered micromobility infrastructure typically shows positive returns within 4-5 years through reduced operational costs and increased user adoption rates.
Public Transport Integration
Modern urban solar power installations are increasingly being integrated with existing public transportation infrastructure to create sustainable, efficient mobility networks. These integrated systems facilitate seamless connections between solar-powered public transportation and traditional transit options, enhancing the overall efficiency of urban mobility.
Solar-equipped transport hubs typically feature charging stations for electric buses and trains, powered by rooftop solar arrays and enhanced by smart grid technology. These hubs serve as connection points where passengers can transition between different modes of transportation while the facility generates clean energy to offset its operational costs.
Key integration features include real-time digital displays powered by solar energy, climate-controlled waiting areas, and electric vehicle charging stations for both public and private transport. The implementation of smart scheduling systems, also powered by on-site solar installations, helps coordinate arrival and departure times across different transportation modes, reducing wait times and improving service reliability.
Many cities have successfully demonstrated that solar-integrated transport hubs can reduce operational costs while improving service quality and environmental performance. These installations typically achieve ROI within 5-7 years while providing long-term benefits to both transit operators and passengers.
Economic and Environmental Impact
ROI Analysis
Urban solar power installations demonstrate compelling financial returns, with most projects achieving payback periods between 5-8 years, depending on local energy costs and available incentives. A typical 100kW commercial rooftop system can generate annual savings of $15,000-$20,000 in electricity costs, while contributing to improved transportation economics through integrated mobility solutions.
Initial investment costs have decreased significantly, with current prices averaging $2-3 per watt installed. Commercial property owners can expect an internal rate of return (IRR) between 10-15% over the system’s 25-year lifespan. Additional financial benefits include:
– Federal tax incentives covering up to 30% of installation costs
– State-specific renewable energy credits
– Increased property value (3-4% on average)
– Reduced maintenance costs compared to traditional energy systems
– Protection against rising utility rates
Real-world analysis from major urban installations shows that solar integration can reduce operational costs by 40-60% when combined with energy storage solutions. Corporate sustainability goals are also met through decreased carbon emissions, with many organizations reporting enhanced brand value and customer loyalty as secondary benefits.
For maximum ROI optimization, facility managers should consider:
– System sizing based on actual energy consumption
– Peak demand reduction strategies
– Available roof space and structural capacity
– Local utility rates and incentive programs
– Maintenance requirements and warranties
Carbon Footprint Reduction
Urban solar power installations significantly reduce carbon emissions by replacing traditional energy sources with clean, renewable solar energy. Recent studies indicate that a typical commercial solar installation can offset approximately 1,000 metric tons of CO2 emissions annually, equivalent to removing 200 cars from the road.
In dense urban environments, rooftop solar arrays deliver particularly impressive environmental benefits. A 100kW commercial system can prevent the release of up to 150,000 pounds of carbon dioxide each year while reducing dependence on fossil fuels. Moreover, urban solar installations help combat the heat island effect by absorbing solar radiation that would otherwise be converted to heat in city environments.
Cities implementing large-scale solar initiatives have reported substantial improvements in air quality metrics. For example, the Los Angeles Solar Initiative achieved a reduction of 3.6 million metric tons of carbon emissions in its first decade of operation. Similar programs in New York City demonstrate that urban solar installations can reduce building-related emissions by up to 40% when combined with energy efficiency measures.
The lifecycle analysis of urban solar systems shows that the carbon footprint of manufacturing and installation is typically offset within the first three years of operation. With an average system lifespan of 25-30 years, this represents decades of positive environmental impact. Additionally, modern recycling programs for solar panels ensure that up to 95% of materials can be recovered and repurposed, further enhancing the sustainability profile of urban solar installations.
Implementation Case Study
The Denver Transit Hub Solar Initiative stands as a compelling example of successful urban solar power implementation in transportation infrastructure. Launched in 2019, this comprehensive project transformed the Central Station transit hub into a model of sustainable energy integration, serving over 100,000 daily commuters while generating clean power for facility operations.
The installation encompasses 2,500 solar panels across the hub’s 45,000-square-foot rooftop and adjacent parking structures, generating 1.2 megawatts of power annually. This system provides 85% of the facility’s total energy requirements, including charging stations for electric buses, climate control, and lighting systems.
Key implementation strategies included:
– Phased installation to minimize disruption to daily operations
– Integration with existing power infrastructure through smart grid technology
– Installation of energy storage systems for consistent power supply
– Development of a comprehensive monitoring and maintenance program
The financial outcomes have exceeded initial projections. With an initial investment of $4.2 million, the project achieved break-even within 5.5 years through energy cost savings and federal tax incentives. Current annual energy savings amount to $425,000, with additional revenue generated from excess power sold back to the grid.
Environmental benefits have been equally impressive. The system reduces carbon emissions by 1,200 metric tons annually, equivalent to removing 260 cars from the road. The project has also improved air quality in the surrounding urban area and created 35 permanent maintenance and operations jobs.
The success of this implementation has led to several key learnings:
– Early stakeholder engagement is crucial for project success
– Weather pattern analysis helps optimize panel placement and angle
– Regular maintenance schedules ensure optimal system performance
– Public education programs increase community support and engagement
The Denver Transit Hub project demonstrates how urban solar power can effectively transform traditional transportation infrastructure into sustainable energy centers. Its success has inspired similar initiatives in five other major U.S. cities, establishing a replicable model for urban solar mobility hubs nationwide.
The integration of solar power into urban mobility hubs represents a transformative shift in how cities approach sustainable transportation infrastructure. These solar-powered facilities serve as powerful examples of how renewable energy can effectively support and enhance urban mobility while delivering substantial environmental and economic benefits. By combining charging stations, energy storage systems, and smart grid technologies, these hubs demonstrate the viability of solar power in meeting the growing demands of electric vehicle adoption and public transportation needs.
The success of implemented projects across various cities has proven that solar-powered mobility hubs can significantly reduce operational costs while providing reliable, clean energy for transportation services. These installations have shown remarkable resilience during peak demand periods and have helped municipalities achieve their sustainability goals while creating more resilient urban infrastructure.
Looking ahead, the continued advancement of solar technology, coupled with decreasing installation costs and improved energy storage solutions, positions solar-powered mobility hubs as a cornerstone of future urban development. Their potential to create energy-independent transportation networks while reducing carbon emissions makes them an essential component of smart city initiatives.
As more cities transition toward sustainable transportation solutions, solar-powered mobility hubs will play an increasingly vital role in shaping urban landscapes, supporting electric mobility, and fostering more sustainable communities. The demonstrated success of existing implementations provides a clear roadmap for other municipalities and organizations looking to embrace this innovative approach to urban transportation infrastructure.

